Undergraduate Program for Electronic Information Engineering
I. Objectives
Students are nurtured to be senior engineers of electronic information engineering, with a solid natural science knowledge, a good sense of social responsibility, systematic professional knowledge, as well as the ability to perform critically and innovatively, an orientation towards life-long learning, participation in international cooperation and competition. Graduates will be engaged in applied research, technology development, operation and management, teaching and research of computer information processing and electronic equipment manufacturing in the field of electronic information and rail transportation.
II. Educational Profile
1. Engineering knowledge: students can use mathematics, natural sciences, electronic information and professional knowledge to describe, analyze and solve complex engineering problems in the field of electronic information engineering.
2. Problem analysis: students can apply the basic principles of mathematics, natural science and engineering science to draw valid conclusions by recognition, expression, and literature research analysis of complex engineering problems in the field of electronic information engineering.
3. Design/develop solution: students can innovatively design solutions for complex engineering problems in the field of electronic information engineering, to meet the specific needs of the system, unit (parts), with the consideration of social, health, safety, legal, cultural and environmental factors.
4. Research: students can draw the reasonable and effective conclusions by researches on complex electronic information engineering problems, including experimental design, data analysis and interpretation on the scientific principles and scientific method.
5. The application of modern tools: students can develop, select and use the appropriate technology, resources and modern engineering tools and information tools, including the prediction and simulation of complex electronic information engineering problems, to solve problems and to understand its limitations.
6. Engineering and society: students can reasonably analyze and evaluate the social, health, safety, legal and cultural influences on the electronic information engineering projects and solutions, and undertake the responsibility.
7. Environmental and sustainable development: students can understand and evaluate the impact of engineering practices on complex engineering issues to environmental and social sustainable development.
8. Professional norms: students are expected to have a value for humanistic pursuits and a sense of social responsibility, ability to understand and comply with the professional ethics and norms, ability to correctly perform their responsibilities.
9. Individuals and teams: students can role as individuals, team members, and leaders in multiple-disciplines engineering projects or in the technical teams.
10. Communication: students can effectively communicate the engineering problems with the industry peers and the social public, including reports writing, documents design, presentation, clear expression or respond to commands. With a certain international vision, students can communicate and communicate in a cross-cultural context.
11. Project management: students can understand and master engineering management principles and economic decision-making methods, and can apply those methods in multidisciplinary disciplines.
12. Lifelong learning: students have an awareness of self-learning and lifelong learning, and the ability to further study and adapt to development.
III. Duration of Schooling and Conferred Degree
Duration of Schooling: 4 years
Conferred Degree: Bachelor of Engineering
IV. Main Courses and Core Disciplines
Main Courses:
Electrical engineering, control science and engineering, computer science and technology.
Discipline foundation courses:
Advanced Mathematics, Fundamentals of Physics, Linear Algebra, Complex Functions and Integral Transformations, Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics,Mechanical Drawing, Electric Circuits, Analogue Electronic Technology, Signals and Systems, Principles of Automatic Control, Principles of Micro-Computer.
Basic courses:
Information Theory and Coding, Fundamentals of Computer Programming, Digital Signal Processing, Computer Networks,
Courses for Electronic Measurement and Control Technology:
Sensors and Signal Detection Technology, Power Electronics, Fundamentals of Electrical Machinery, Computer Control Technology.
Courses for Computer Information Processing:
Operating System, Object-Oriented Programming, System Modeling and Simulation, Architecture of Railway Information Systems.
V. The Minimum Credits Requirements for Graduation
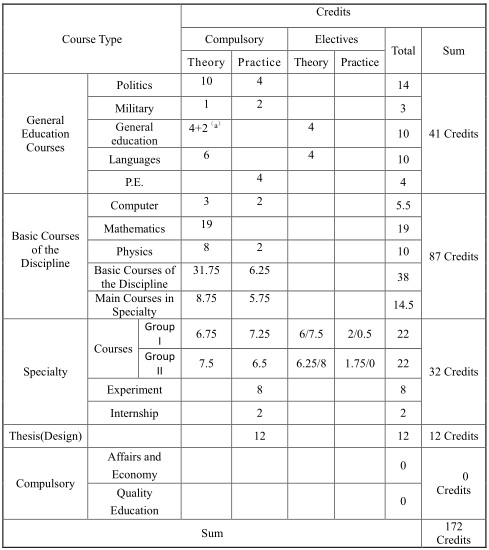
Note: orientation and Seminars with 2 credits are set in the first semester with a variety of courses in the electives.
VI. An Omnibus Schedule for Courses
An Omnibus Schedule for Courses.pdf
Note: Innovation Practice with 2 credits should be executed in line with the collegiate regulations; those who fail to pass CET 4 have to choose English III and one of other language electives.
Compulsory Courses
Name |
Course Type |
Credits |
Note |
Affairs and Economy |
compulsory |
0 |
16 hours each semester, from semester 1 to semester 7 |
Quality Education |
compulsory |
0 |
Requirements in details:http://youth.swjtu.edu.cn/ShowNews- 37385-1.shtml |
Electronic Information Engineering Course Description.pdf
